What is Svelte and How to get started with SvelteKit
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Svelte
- Benefits of Svelte
- Svelte components
- Reactivity
- SvelteKit
- Getting started with SvelteKit
- Svelte community and resources
Introduction
In the modern era of web development, there has been a surge of powerful frameworks and libraries designed to simplify the creation of web applications. Among these, Svelte stands out as a truly unique and game-changing tool. In this article, we’ll explore the innovative world of Svelte, its key features, and how you can get started with SvelteKit – the official framework for building Svelte applications. As you progress through this guide, you’ll gain a solid understanding of Svelte’s capabilities and learn how to harness its power to build blazingly fast and highly interactive web applications. So, let’s dive into the remarkable realm of Svelte and SvelteKit, and begin your journey towards becoming a proficient Svelte developer!
Frontend Performance
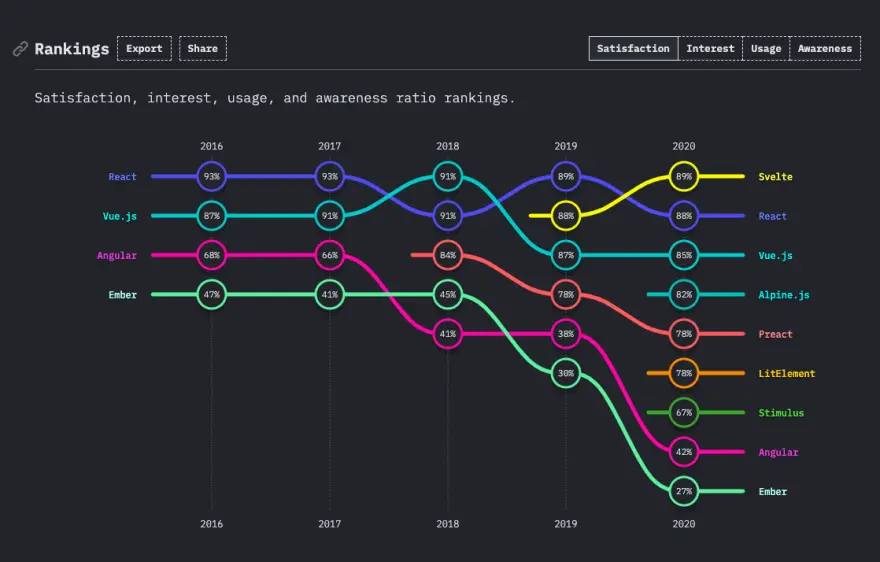
Backend Performance
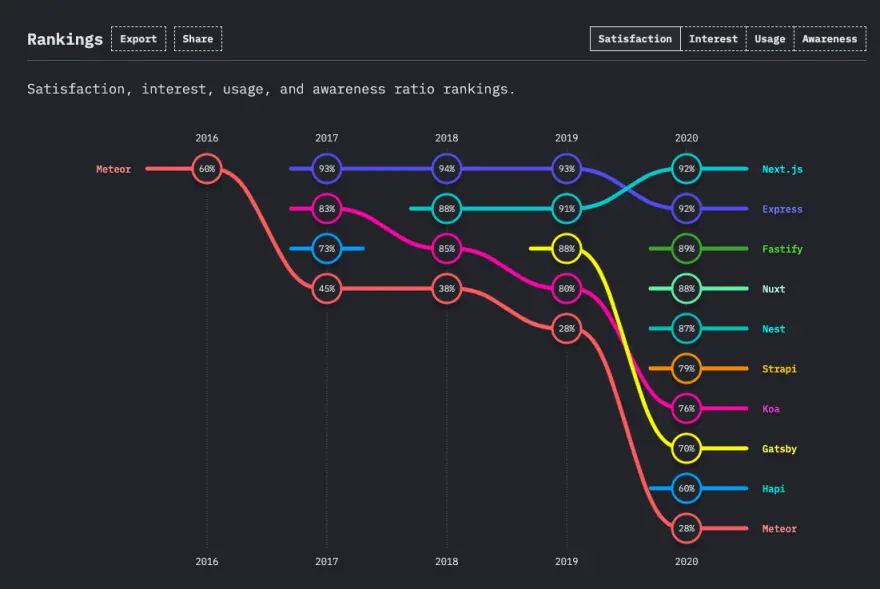
Rethinking Reactivity
Check out this video from Rich Harris, filled with his vision for Svelte and SvelteKit.
👇🏽
When covering Svelte and SvelteKit, here are some key points you should address:
What is Svelte
Svelte is an innovative, compiler-based framework designed for building highly performant and interactive user interfaces. Created by Rich Harris, a graphics editor at the New York Times, Svelte has quickly gained traction among developers for its unique approach to web application development. Unlike traditional frameworks like React and Vue, which rely on a runtime library to manage and update the DOM, Svelte operates at compile time, generating highly optimized JavaScript code that updates the DOM directly.
Svelte’s unique approach brings several benefits, as it does not require a virtual DOM or additional runtime libraries. This results in smaller bundle sizes, faster initial load times, and improved overall performance. Svelte applications are, therefore, well-suited for scenarios where performance and user experience are critical factors.
The key difference between Svelte and its counterparts lies in its architecture. While React and Vue use a virtual DOM to manage updates and optimize performance, Svelte eliminates the need for this intermediary layer by compiling components down to vanilla JavaScript code. This code is specifically tailored to update the DOM efficiently when the application’s state changes, leading to a more direct and streamlined interaction with the browser.
In summary, Svelte is a groundbreaking compiler-based framework that enables developers to build highly efficient and interactive user interfaces. Its creator, Rich Harris, has fundamentally challenged the traditional virtual DOM approach, setting Svelte apart from other popular frameworks like React and Vue. By leveraging the power of compile-time optimizations, Svelte delivers exceptional performance and user experiences, making it an exciting choice for modern web development.
Benefits of Svelte
Svelte offers numerous advantages over traditional web development frameworks, which make it an attractive choice for building modern web applications. Here are some key benefits of using Svelte:
-
Smaller bundle sizes: Svelte’s compile-time approach generates highly optimized JavaScript code, which directly manipulates the DOM without the need for an additional runtime library. This results in significantly smaller bundle sizes, reducing the amount of data that needs to be transferred and parsed by the browser.
-
Faster load times: Smaller bundle sizes directly contribute to faster load times, as the browser has less code to download, parse, and execute. This leads to a quicker rendering of the initial view, providing a better user experience, especially on slower networks and less powerful devices.
-
Improved performance: Svelte’s compile-time optimizations generate code tailored to efficiently update the DOM as the application’s state changes. This eliminates the need for a virtual DOM, which is used by frameworks like React and Vue to manage updates and improve performance. By directly updating the DOM, Svelte applications can respond more quickly to user interactions and state changes, delivering a smoother and more responsive experience.
-
Efficient code execution: Svelte’s compiler intelligently analyzes components and removes any unused code, ensuring that only the necessary code is executed at runtime. This process, known as tree-shaking, contributes to a leaner and more efficient codebase, further enhancing the performance of Svelte applications.
-
Simplified developer experience: Svelte components are written in a single .svelte file, which combines HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. This makes it easier to understand and maintain the code, reducing the cognitive load on developers and enabling them to work more efficiently.
-
Reactive by design: Svelte’s reactivity system allows developers to automatically update the DOM when data changes, without the need for complex state management libraries or additional boilerplate code. This leads to more maintainable and easy-to-understand code, simplifying the process of building complex applications.
In summary, Svelte provides several notable benefits, including smaller bundle sizes, faster load times, improved performance, and more efficient code execution. Its compile-time approach and the elimination of the virtual DOM lead to a more direct and streamlined interaction with the browser, resulting in a better overall user experience and simplified development process.
Svelte components
Svelte components are the fundamental building blocks of Svelte applications. They are self-contained, reusable pieces of UI that encapsulate the structure, appearance, and behavior of a specific part of the application. Svelte components enable developers to create modular and maintainable code, promoting better organization and separation of concerns.
Components in Svelte are written in .svelte files, which combine HTML, CSS, and JavaScript within a single file. This approach simplifies the development process, making it easier to understand and manage the code related to a particular component. A typical Svelte component file consists of three main sections:
HTML (Structure)
The HTML section defines the structure and layout of the component. It includes standard HTML tags, as well as custom Svelte-specific syntax, such as directives and bindings, which enable dynamic updates and interactions with the component’s state.
Example
<div>
<h1>Hello, {name}!</h1>
<button on:click={handleClick}>Click me</button>
</div>
CSS (Appearance)
The CSS section is responsible for styling the component. It defines the visual appearance of the component, such as colors, fonts, and layouts. In Svelte, the CSS is scoped by default, meaning that the styles will only apply to the specific component and won’t leak to other parts of the application.
Example:
<style>
h1 {
color: blue;
}
button {
background-color: red;
color: white;
}
</style>
JavaScript (Behavior)
The JavaScript section defines the component’s behavior and manages its state. It includes variables, functions, and reactive declarations that determine how the component responds to user interactions and updates its state.
Example:
<script>
let name = 'World';
function handleClick() {
name = 'Svelte';
}
</script>
By combining these three sections in a single .svelte file, developers can create modular and easy-to-understand components. This structure encourages a clear separation of concerns and promotes better organization of the codebase, resulting in more maintainable and scalable applications.
In summary, Svelte components are the essential building blocks of Svelte applications, combining the structure, appearance, and behavior of a specific part of the UI in a single .svelte file. This approach simplifies the development process, promotes modularity and maintainability, and helps developers create well-structured and efficient applications.
Reactivity
Svelte’s reactivity system is one of its most powerful and distinguishing features. Reactivity refers to the automatic updating of the DOM when the underlying data changes, enabling components to stay in sync with the application’s state without manual intervention. Svelte’s approach to reactivity is unique, as it is built into the language itself, simplifying the development process and leading to more efficient code execution.
Here are some key concepts and mechanisms related to reactivity in Svelte:
Reactive assignments
In Svelte, reactivity is achieved by using reactive assignments, which are denoted with a special syntax – a single $ followed by a colon ($:). Whenever a variable involved in a reactive assignment changes, Svelte will automatically update the DOM and recompute any dependent values.
Example:
<script>
let count = 0;
let doubledCount = 0;
const addCount = () => {
count ++
}
$: doubledCount = count * 2;
$: sum = doubledCount + count
</script>
<p>
{count} + {doubledCount} = {sum}
</p>
<button on:click={addCount}>
Add Count
</button>
In this example, doubledCount will automatically update whenever count changes, and the DOM will be updated accordingly.
Reactive statements
Reactive statements are similar to reactive assignments but allow for more complex logic and side effects. They are also denoted with the $: syntax and will be re-run whenever any of their dependencies change.
Example:
<script>
let count = 0;
$: {
console.log(`The count has changed to ${count}`);
}
</script>
In this example, the console log statement will be executed whenever count changes.
Reactive declarations
Reactive declarations are a shorthand way to create reactive assignments. Instead of explicitly using the $: syntax, you can declare a variable as reactive by prefixing it with the $ symbol. This makes the variable’s value automatically update whenever its dependencies change.
Example:
<script>
import {writable} from 'svelte/store';
export const count = writable(0);
$: doubledCount = $count * 2
const addToCount = () => {
$count ++
}
</script>
count: {$count} <br/>
doubledCount: {doubledCount} <br/>
<button on:click="{addToCount}" >
Add
</button>
In this example, doubledCount will automatically update whenever the value of the count store changes.
Svelte’s reactivity system is built on the principle of minimal updates, meaning that it only updates the parts of the DOM that actually change. This results in highly efficient and performant applications, as unnecessary updates and re-renders are avoided.
In summary, Svelte’s unique approach to reactivity allows for automatically updating the DOM when data changes, simplifying the development process and leading to more efficient code execution. Reactive statements, assignments, and variables are the key mechanisms used to achieve this reactivity, ensuring that components stay in sync with the application’s state and respond efficiently to user interactions.
SvelteKit
SvelteKit is the official framework for building Svelte applications, designed to streamline the development and deployment process while providing a powerful set of features that cater to various use cases. It is a full-featured and flexible framework that enhances Svelte by offering tools for server-side rendering (SSR), static site generation (SSG), and a flexible file-based routing system, among other features.
Here are some key features of SvelteKit:
-
Server-Side Rendering (SSR): SvelteKit allows developers to perform server-side rendering, which means that the HTML content of the application is generated on the server before being sent to the client. This results in faster load times, improved search engine optimization (SEO), and better compatibility with social media sharing and link previews.
-
Static Site Generation (SSG): SvelteKit also supports static site generation, which is the process of rendering a site’s pages ahead of time, during the build process. This enables the creation of fast and highly performant static sites that can be easily deployed to a variety of hosting services. Static sites are a great fit for projects like blogs, documentation sites, and marketing pages.
-
Flexible file-based routing: SvelteKit features a file-based routing system, which allows developers to create routes for their application by simply organizing their Svelte components into a hierarchical folder structure. This approach simplifies the routing process and makes it easier to understand and manage the application’s structure.
-
Built-in development server: SvelteKit includes a built-in development server that provides features like hot module replacement (HMR), which allows developers to see their changes in real-time without having to refresh the page manually. This speeds up the development process and improves the overall developer experience.
-
Adapter system: SvelteKit’s adapter system enables developers to easily deploy their applications to various hosting platforms, such as Vercel, Netlify, and even custom servers. Adapters are plugins that handle the build output and deployment process, ensuring a smooth transition from development to production.
-
API routes: SvelteKit supports the creation of API routes, which allows developers to build serverless functions and backend logic directly within their application. This simplifies the process of creating full-stack applications, as both frontend and backend logic can be managed in a single codebase.
By offering these features, SvelteKit streamlines the development and deployment process for Svelte applications, making it easier for developers to build, test, and deploy their projects. Its built-in tools, such as server-side rendering, static site generation, and a flexible file-based routing system, cater to a wide range of use cases and ensure that Svelte applications are fast, performant, and easy to maintain.
In summary, SvelteKit is the official framework for building Svelte applications, offering a powerful set of features that streamline the development and deployment process. With its support for server-side rendering, static site generation, and a flexible file-based routing system, SvelteKit enables developers to build fast, performant, and scalable applications with ease.
Getting started with SvelteKit
To set up a new SvelteKit project, follow these step-by-step instructions:
Installation
Ensure that you have Node.js (version 12.x or higher) installed on your system. Open a terminal or command prompt, and run the following command to install the SvelteKit package globally:
I use pnpm instead of npm because it’s faster and more efficient.
npm create svelte@latest my-sveltekit-app
Setup a new project
- Select
Skeleton projectas the starter template, - Then Select
TypeScriptas the language. (I prefer TypeScript over JavaScript) - Select
EsLintas the linter. - Select
Prettieras the formatter. - Select
Playwrightas the testing framework. - Select
Vitestas the unit testing.
Navigate to your newly created project directory:
cd my-sveltekit-app
Install dependencies Run the following command to install the necessary dependencies for your SvelteKit project:
npm install
Start the development server
Run the following command to start the SvelteKit development server:
npm run dev
You can now access your SvelteKit application in your browser at http://localhost:3000.
Understand the project structure
Familiarize yourself with the default SvelteKit project structure:
src: Thesrcdirectory contains your application’s source code, including components and routes.src/routes: Theroutesdirectory is where you’ll create your application’s pages and routes, using the file-based routing system.src/lib: Thelibdirectory is a place for shared utility functions and components that are used across your application.static: Thestaticdirectory contains static assets, such as images, fonts, and stylesheets, which will be served directly by the server.
Create components
To create a new Svelte component, simply create a new .svelte file in the src/lib or src/routes directory, depending on whether it’s a shared component or a route-specific component. Write your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code within the appropriate sections of the .svelte file.
Add routes
To add a new route to your application, create a new .svelte file in the src/routes directory. The file’s name and location within the directory structure will determine the URL for the route. For example, to create a route for /about, create a file named About.svelte inside the src/routes directory.
Configure your application
You can configure your SvelteKit application by modifying the svelte.config.js file. This file contains settings for adapters, SSR, and other build and runtime options.
Build and deploy
Once you have finished developing your application, you can build it for production using the following command:
npm run build
To deploy your application, follow the instructions provided by your chosen hosting platform, and use the appropriate SvelteKit adapter to configure the deployment process.
By following these steps, you can set up a new SvelteKit project, create components, add routes, and deploy your application. This will give you a solid foundation to build upon as you develop your Svelte application and explore the full potential of SvelteKit.
Svelte community and resources
The Svelte community is a growing and supportive ecosystem of developers, contributors, and enthusiasts who share a passion for building efficient and performant web applications using the Svelte framework. The community offers various resources, including documentation, tutorials, and forums, to help developers deepen their understanding of Svelte and SvelteKit.
Here are some valuable resources to help you get started and enhance your Svelte and SvelteKit knowledge:
-
Official Svelte Documentation: The official Svelte documentation (https://svelte.dev/docs) is a comprehensive and well-structured guide that covers everything from the basics to advanced topics. It provides detailed explanations, examples, and interactive demos to help you understand the core concepts and best practices.
-
Official SvelteKit Documentation: The official SvelteKit documentation (https://kit.svelte.dev/docs) offers a complete guide to building applications with SvelteKit. It covers topics such as project setup, routing, server-side rendering, static site generation, deployment, and more.
-
Svelte REPL: The Svelte REPL (https://svelte.dev/repl) is an interactive online editor that allows you to create, edit, and share Svelte components directly in your browser. It is an invaluable tool for experimenting with Svelte concepts, debugging your code, and learning from others.
-
Svelte Society: Svelte Society (https://sveltesociety.dev/) is a community-driven initiative that aims to bring together Svelte developers from around the world. They organize meetups, conferences, and other events, and curate a collection of resources, including articles, videos, and examples.
-
Svelte Discord: The Svelte Discord server (https://svelte.dev/chat) is a great place to connect with other Svelte developers, ask questions, share your experiences, and get help with any issues you encounter while working with Svelte or SvelteKit.
-
Svelte subreddit: The Svelte subreddit (https://www.reddit.com/r/sveltejs/) is another platform where you can engage with the Svelte community, share your projects, ask questions, and stay up-to-date with the latest news and developments related to Svelte.
-
Svelte YouTube channel: The official Svelte YouTube channel (https://www.youtube.com/c/SvelteMaster) features video tutorials, conference talks, and other educational content to help you expand your knowledge and skills in Svelte and SvelteKit.
-
Svelte Tutorials and Courses: Numerous online tutorials and courses are available to learn Svelte and SvelteKit, ranging from beginner to advanced levels. Some popular platforms offering Svelte courses include freeCodeCamp, Udemy, and Frontend Masters.
By leveraging these resources and actively participating in the Svelte community, you can deepen your understanding of Svelte and SvelteKit, stay informed about the latest developments, and get the support you need to build efficient, performant, and scalable web applications.
In conclusion, Svelte, along with its official framework SvelteKit, offers a refreshing and innovative approach to building web applications with an emphasis on efficiency, performance, and simplicity. Its unique compile-time optimization and built-in reactivity system set it apart from other popular frameworks like React and Vue, making it an attractive choice for developers seeking to create modern, fast, and scalable web applications.
The growing Svelte community provides a wealth of resources, including documentation, tutorials, and forums, to support developers as they learn and work with Svelte and SvelteKit. By taking advantage of these resources and the community’s collective knowledge, developers can unlock the full potential of Svelte and SvelteKit, ultimately delivering outstanding user experiences on the web.
Whether you are a seasoned developer or just starting your journey in web development, exploring Svelte and SvelteKit offers a valuable opportunity to expand your skillset, stay current with industry trends, and contribute to the ongoing evolution of web development practices.